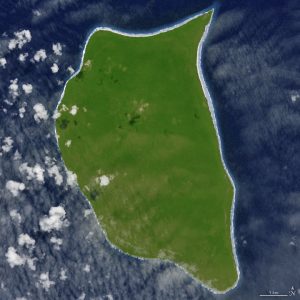
This image was acquired by the Advanced Spaceborne Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) aboard the Terra satellite. Relatively cloud-free, the image shows a perimeter of narrow beaches surrounding a mostly flat, vegetation-covered island that spans 14 square miles (37 square kilometers). (Credit: NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen, using data from NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team)
In the middle of the South Pacific Ocean, far from the urban, developed world, there’s a small, lush, green island with white sand beaches. However, this uninhabited, remote corner of the tropics—Henderson Island—also has a trash problem.
The beaches of Henderson Island have the highest density of plastic waste in the world, according to a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Since the island is located near the center of an ocean gyre, it’s in an ideal position to collect trash floating by on currents from the Americas.
Even as other Pacific islands have seen development, Henderson has remained largely free of human activity. It contains poor soil and is located roughly 125 miles (200 kilometers) from the closest inhabited island. The absence of people has been a boon for wildlife, as the island shelters a bunch of endemic species, including 10 plants and four land birds unique to the island.
