What are the effects of the “angle between images” setting in circular missions when it comes to 3D reconstruction?
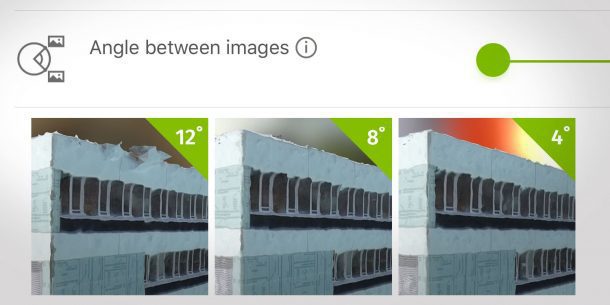
Knowing which drone flight plan to design for 3D modeling can be challenging, but the good news is that Pix4Dcapture has automatic flight missions optimized for different scenarios. We tested circular missions with three image angle overlay variations in order to compare results.
Circular missions are recommended to 3D map a single object of interest, like a building or a monument.
When it comes to circular mission settings, DJI drone pilots can choose the angle between images. By dividing the 360° flight covered by the drone into sections, or variable angles (4°, 8°, 12°), the drone is told by the app to shoot a picture when it reaches the predefined angle. At a practical level, this means that at a low angle value (e.g. 4°), the drone will take more images and have a bigger image overlap than a higher angle value (e.g. 12°).

For this test, we flew the three missions around a building with a base of 30 x 30 meters and height of 18 meters, using a DJI Phantom 4.
Each mission had a different value for the “angle between images” setting; we tested capturing images with 4°, 8° and 12°. As constant factors, the flight altitude was 40m and the data was processed on Pix4D Cloud.
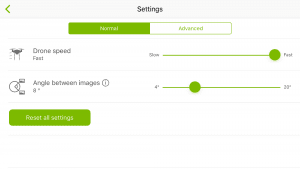
Circular mission with 4° angle between images
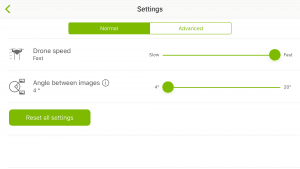
Circular mission with 8° angle between images
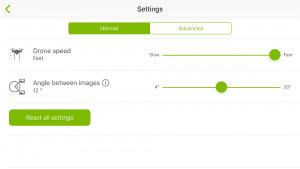
Circular mission with 12° angle between images
So, how do I choose the angle between images in circular flights?
To answer this question, it’s important to define the goal of your 3D mapping project and keep in mind time and quality constraints.
By using a higher overlay level, there is more image information for the software to reconstruct an object, resulting in a more detailed 3D model. However, more data implies more time spent flying and acquiring images, and also a longer processing time.
Depending on the purpose of the 3D model, managing the angle between images helps balance time and quality: allowing you to choose from faster and more schematic reconstructions, to more detailed ones.
So, what are your project goals and constraints?