 Launched just two months ago and still in the process of being commissioned for service, the Copernicus Sentinel-1C satellite is, remarkably, already showing how its radar data can be used to map the shape of Earth’s land surface with extreme precision.
Launched just two months ago and still in the process of being commissioned for service, the Copernicus Sentinel-1C satellite is, remarkably, already showing how its radar data can be used to map the shape of Earth’s land surface with extreme precision.
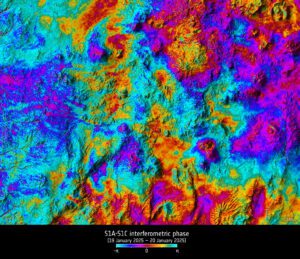
These first cross-satellite “interferometry” results assure its ability to monitor subsidence, uplift, glacier flow, and disasters such as landslides and earthquakes.
This cross-satellite interferogram is of the Atacama Desert plateau in northern Chile and was generated from images acquired just one day apart, by Sentinel-1A on Jan. 19, 2025, and Sentinel-1C on Jan. 20, 2025.
Image Credit: Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2025), processed by DLR Microwaves & Radar Institute/ESA
