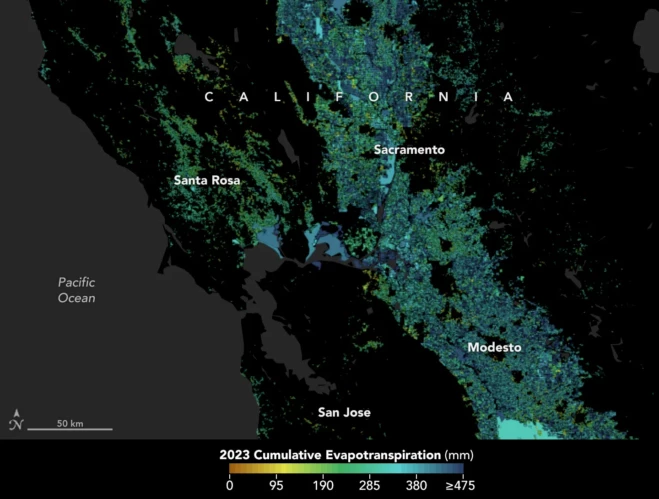
In California, state officials and farmers are using satellite data through OpenET to track evapotranspiration to better manage water resources. The process is a window into the water consumed by plants and crops, such as those grown in the Central Valley. (Credit: NASA Earth Observatory using openetdata.org)
As the world looks for sustainable solutions, a system tapping into NASA satellite data for water management has passed a critical test.
Called OpenET, the system uses an ensemble of six satellite-driven models that harness publicly available data from the Landsat program to calculate evapotranspiration (ET)—the movement of water vapor from soil and plant leaves into the atmosphere. OpenET does this on a field-level scale that’s greatly improving the way farmers, ranchers, and water resource managers steward one of Earth’s most precious resources.
Researchers have now conducted a large-scale analysis of how well OpenET is tracking evapotranspiration over crops and natural landscapes. The team compared OpenET data with measurements from 152 sites with ground-based instruments across the United States. In agricultural areas, OpenET calculated evapotranspiration with high accuracy, especially for annual crops such as wheat, corn, soy, and rice. The researchers reported their findings on Jan. 15, 2024, in Nature Water.
There are no upcoming events.
