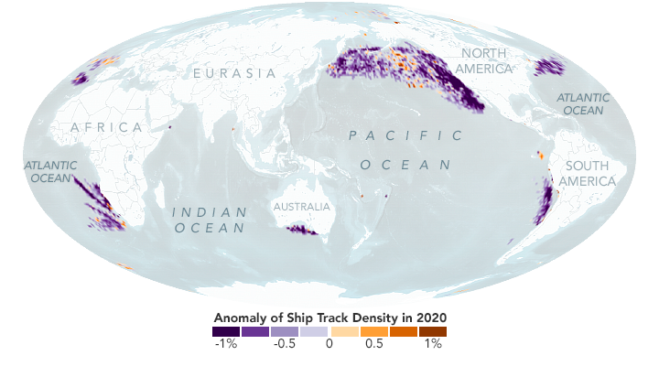
 Ship tracks, the polluted marine clouds that trail ocean-crossing vessels, are a signature of modern trade. Like ghostly fingerprints, they trace shipping lanes around the globe, from the North Pacific to the Mediterranean Sea. But in 2020, satellite observations showed fewer of those pollution fingerprints.
Ship tracks, the polluted marine clouds that trail ocean-crossing vessels, are a signature of modern trade. Like ghostly fingerprints, they trace shipping lanes around the globe, from the North Pacific to the Mediterranean Sea. But in 2020, satellite observations showed fewer of those pollution fingerprints.
Drawing on nearly two decades of satellite imagery, researchers found that the number of ship tracks fell significantly after a new fuel regulation went into effect. A global standard implemented in 2020 by the International Maritime Organization (IMO)–requiring an 86% reduction in fuel sulfur content–likely reduced ship track formation. COVID-19-related trade disruptions also played a small role in the reduction.
Scientists used advanced computing techniques to create the first global climatology (a history of measurements) of ship tracks. They used artificial intelligence to automatically identify ship tracks across 17 years of daytime images (2003-2020) captured by NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite.
Image Credit: NASA Earth Observatory
There are no upcoming events.
