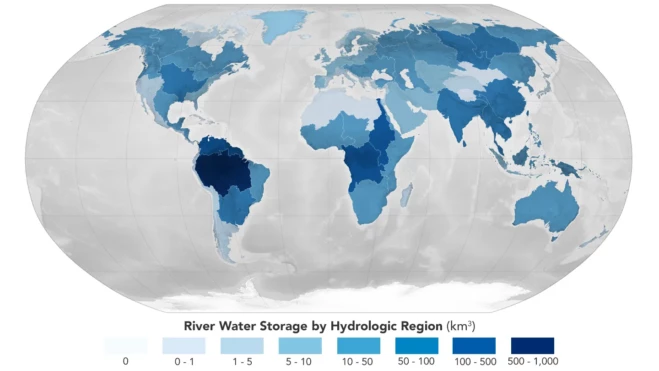
 A study led by NASA researchers provides new estimates of how much water courses through Earth’s rivers, the rates at which it’s flowing into the ocean, and how much both of those figures have fluctuated over time—crucial information for understanding the planet’s water cycle and managing its freshwater supplies. The results also highlight regions depleted by heavy water use, including the Colorado River basin in the United States, the Amazon basin in South America, and the Orange River basin in southern Africa.
A study led by NASA researchers provides new estimates of how much water courses through Earth’s rivers, the rates at which it’s flowing into the ocean, and how much both of those figures have fluctuated over time—crucial information for understanding the planet’s water cycle and managing its freshwater supplies. The results also highlight regions depleted by heavy water use, including the Colorado River basin in the United States, the Amazon basin in South America, and the Orange River basin in southern Africa.
For the study, which was recently published in Nature Geoscience, researchers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California used a novel methodology that combines stream-gauge measurements with computer models of about 3 million river segments around the world.
It estimated that the Amazon basin contains about 38% of the world’s river water, the most of any hydrological region evaluated.
Image Credit: NASA
There are no upcoming events.
