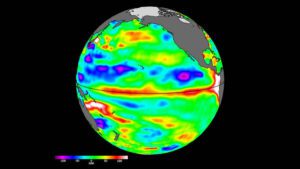
Sea-level data from the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite on April 24, 2023, shows relatively higher (shown in red and white) and warmer ocean water at the equator and the west coast of South America. Water expands as it warms, so sea levels tend to be higher in places with warmer water. (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
The most recent sea-level data from the U.S.-European satellite Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich indicates early signs of a developing El Niño across the equatorial Pacific Ocean. The data shows Kelvin waves, which are roughly 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 centimeters) high at the ocean surface and hundreds of miles wide, moving from west to east along the equator toward the west coast of South America.
When they form at the equator, Kelvin waves bring warm water, which is associated with higher sea levels, from the western Pacific to the eastern Pacific. A series of Kelvin waves starting in spring is a well-known precursor to an El Niño, a periodic climate phenomenon that can affect weather patterns around the world. It is characterized by higher sea levels and warmer-than-average ocean temperatures along the western coasts of the Americas.
Water expands as it warms, so sea levels tend to be higher in places with warmer water. El Niño is also associated with a weakening of the trade winds. The condition can bring cooler, wetter conditions to the U.S. Southwest and drought to countries in the western Pacific, such as Indonesia and Australia.
