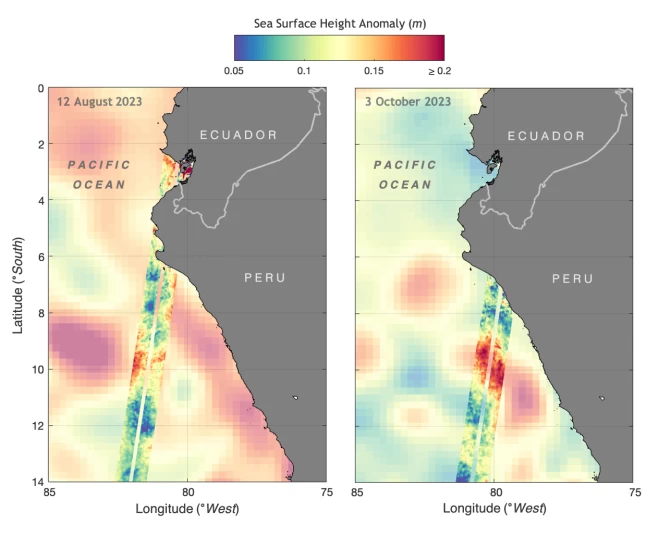
Data from the SWOT satellite shows sea level anomalies—how much higher or lower sea levels are compared to the average height—off the coast of Ecuador and Peru on Aug. 12, 2023, and Oct. 3, 2023. The data indicates the development of an El Niño along the west coast of the Americas. (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
An analysis by NASA’s sea-level change science team finds that if a strong El Niño develops this winter, cities along the western coasts of the Americas could see an increase in the frequency of high-tide flooding that can swamp roads and spill into low-lying buildings.
El Niño is a periodic climate phenomenon characterized by higher-than-normal sea levels and warmer-than-average ocean temperatures along the equatorial Pacific. These conditions can spread poleward along the western coasts of the Americas. El Niño, which is still developing this year, can bring more rain than usual to the U.S. Southwest and drought to countries in the western Pacific like Indonesia. These impacts typically occur in January through March.
The NASA analysis finds that a strong El Niño could result in up to five instances of a type of flooding called a 10-year flood event this winter in cities including Seattle and San Diego. Places like La Libertad and Baltra in Ecuador could get up to three of these 10-year flood events this winter. This type of flooding doesn’t normally occur along the west coast of the Americas outside of El Niño years. The researchers note that by the 2030s, rising seas and climate change could result in these cities experiencing similar numbers of 10-year floods annually, with no El Niño required.
There are no upcoming events.
