 The new Copernicus Sentinel-4 mission has delivered its first images, highlighting concentrations of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and ozone. Despite being preliminary, these images mark a major milestone in the ability to monitor air quality all the way from geostationary orbit, 36,000 kilometers above Earth.
The new Copernicus Sentinel-4 mission has delivered its first images, highlighting concentrations of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and ozone. Despite being preliminary, these images mark a major milestone in the ability to monitor air quality all the way from geostationary orbit, 36,000 kilometers above Earth.
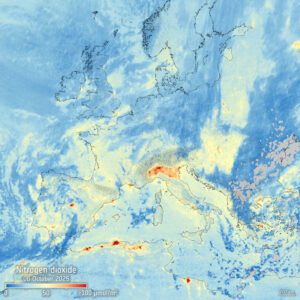
This image depicts tropospheric nitrogen dioxide with clear pollution hotspots visible along the Mediterranean coast and over Italy’s Po Valley. It should be noted that Sentinel-4 cannot measure nitrogen dioxide over areas covered by cloud, which is why the image does not display concentrations over some parts of the map.
Image Credit: Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2025), processed by IUP-Bremen/DLR/ESA
