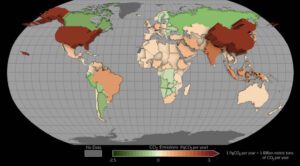
This map shows mean net emissions and removals of carbon dioxide from 2015 to 2020 using estimates informed by NASA’s OCO-2 satellite measurements. Countries where more carbon dioxide was removed than emitted appear as green depressions, while countries with higher emissions are tan or red and appear to pop off the page. (Credit: NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio)
A NASA Earth-observing satellite has helped researchers track carbon dioxide emissions for more than 100 countries around the world. The pilot project offers a powerful new look at the carbon dioxide being emitted in these countries and how much of it is removed from the atmosphere by forests and other carbon-absorbing “sinks” within their borders. The findings demonstrate how space-based tools can support insights on Earth as nations work to achieve climate goals.
The international study, conducted by more than 60 researchers, used measurements made by NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) mission, as well as a network of surface-based observations, to quantify increases and decreases in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations from 2015 to 2020. Using this measurement-based (or “top-down”) approach, the researchers were then able to infer the balance of how much carbon dioxide was emitted and removed.
Although the OCO-2 mission was not specifically designed to estimate emissions from individual nations, the findings from the 100-plus countries come at an opportune time. The first Global Stocktake—a process to assess the world’s collective progress toward limiting global warming, as specified in the 2015 Paris Agreement—takes place in 2023.
