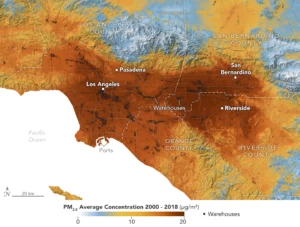
A data visualization shows the average concentration of PM2.5 particulate pollution in the Los Angeles region from 2000 to 2018, along with the locations of nearly 11,000 warehouses. Darker red indicates higher concentration of these toxic particles; small black circles represent warehouse locations. (Credit: NASA Earth Observatory)
As goods of all shapes and sizes journey from factory to doorstep, chances are they’ve stopped at a warehouse along the way—likely several of them. The sprawling structures are waypoints in the logistics networks that make e-commerce possible. Yet the convenience comes with tradeoffs, as illustrated in a recent NASA-funded study.
Published in the journal GeoHealth, the research analyzes patterns of particulate pollution in Southern California and found that ZIP codes with more or larger warehouses had higher levels of contaminants over time than those with fewer or smaller warehouses. Researchers focused on particulate pollution, choosing Southern California because it is a major distribution hub for goods: Its ports handle 40% of cargo containers entering the country.
The buildings themselves are not the major particulate sources. Rather, it’s the diesel trucks that pick up and drop off goods, emitting exhaust containing toxic particles called PM2.5. At 2.5 micrometers or less, these pollutants can be inhaled into the lungs and absorbed into the bloodstream. Although atmospheric concentrations are typically so small they’re measured in millionths of a gram per cubic meter, the authors caution that there’s no safe exposure level for PM2.5.
