 The Amazon basin is exceptional. It spans at least 6 million square kilometers (2.3 million square miles), nearly twice the size of India. It is home to Earth’s largest rainforest as well as the largest river for the volume of the flow and the size of the drainage basin.
The Amazon basin is exceptional. It spans at least 6 million square kilometers (2.3 million square miles), nearly twice the size of India. It is home to Earth’s largest rainforest as well as the largest river for the volume of the flow and the size of the drainage basin.
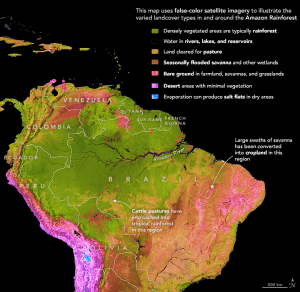
The rainforest, which covers about 80 percent of the basin, is home to one-fifth of the world’s land species, including many found nowhere else in the world. It is also home to more than 30 million people, including hundreds of indigenous groups and several dozen uncontacted or isolated tribes.
The Amazon rainforest is also an enormous carbon sink—an area that draws down carbon from the atmosphere. It also pumps huge quantities of water into the air through a process called transpiration. Enough moisture rises out of the Amazon to supply vast “flying rivers” and about half of the rain that falls back down on the region, explained Thomas Lovejoy, a professor at George Mason University and a senior fellow at the UN Foundation for Science, Economics, and the Environment.
In spite of its vast size and clear significance to the planet, there is much about the Amazon that remains enigmatic because it is such a complex and challenging place to study. It is just as hard to manage. Surrounded by mountainous plateaus on most sides, much of the basin is remote and difficult to access. It covers about one-third of South America; it spans eight countries and many more state and tribal borders; and it features a mosaic of intersecting and overlapping ecosystems.
Image Credit: NASA Earth Observatory images by Lauren Dauphin, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS/LANCE and GIBS/Worldview, Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey and University of Maryland, and topographic data from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). River data from the World Wildlife Fund HydroSHEDS Project. Amazon biome boundaries using data from Olson, DM, et al. (1998). Brazilian Amazon legal boundaries using data from Potter, C.S, et al. (2003).
