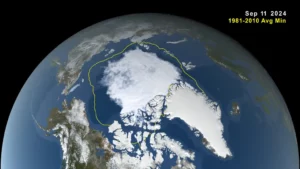
This image, taken from a data visualization, shows Arctic sea ice minimum extent on Sept. 11, 2024. The yellow boundary shows the minimum extent averaged over the 30-year period from 1981 to 2010. (Credit: NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio/Trent L. Schindler)
Arctic sea ice retreated to near-historic lows in the Northern Hemisphere this summer, likely melting to its minimum extent for the year on Sept. 11, 2024, according to researchers at NASA and the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). The decline continues the decades-long trend of shrinking and thinning ice cover in the Arctic Ocean.
The amount of frozen seawater in the Arctic fluctuates during the year as the ice thaws and regrows between seasons. Scientists chart these swings to construct a picture of how the Arctic responds over time to rising air and sea temperatures and longer melting seasons. During the last 46 years, satellites have observed persistent trends of more melting in the summer and less ice formation in winter.
