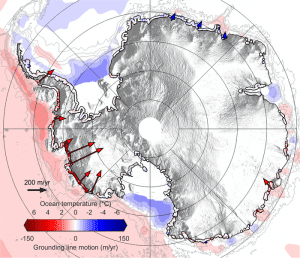
A team of scientists tracked the movement of Antarctica’s grounding line and produced the first complete map showing how this submarine edge is losing its grip on the seafloor. (Credit: CPOM)
The European Space Agency (ESA) CryoSat mission revealed that, during the last seven years, Antarctica has lost an area of underwater ice the size of Greater London. This is because warm ocean water beneath the continent’s floating margins is eating away at the ice attached to the seabed.
Most Antarctic glaciers flow straight into the ocean in deep submarine troughs. The places where their base leaves the seabed and begins to float are known as grounding lines, which typically lie a kilometer or more below sea level and are inaccessible even to submersibles, so remote methods for detecting them are extremely valuable.
A paper published in Nature Geoscience describes how CryoSat was used to map grounding-line motion along 16,000 kilometers of Antarctic coastline. Research led by Hannes Konrad from the Centre for Polar Observation and Modelling at the UK’s University of Leeds shows that between 2010 and 2017, the Southern Ocean melted 1,463 square kilometers of underwater ice.