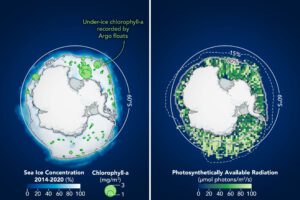
 A decade ago, scientists on a NASA-sponsored ocean expedition found massive populations of phytoplankton blooming beneath sea ice in the Arctic Ocean. Now scientists using underwater instruments and a NASA satellite have found evidence of potentially significant blooms beneath the sea ice encircling Antarctica. The findings were recently published in the scientific journal Frontiers.
A decade ago, scientists on a NASA-sponsored ocean expedition found massive populations of phytoplankton blooming beneath sea ice in the Arctic Ocean. Now scientists using underwater instruments and a NASA satellite have found evidence of potentially significant blooms beneath the sea ice encircling Antarctica. The findings were recently published in the scientific journal Frontiers.
Phytoplankton are to the ocean what grasses are to land: these floating, plant-like organisms soak up sunshine, sponge up mineral nutrients, and create their own food (energy) through photosynthesis. Phytoplankton grow just about anywhere there are open, sunlit patches of ocean. When conditions are right, these collections of microscopic cells can blossom to scales that are visible from space. They are a critical food source for other life in the ocean and a key carbon recycler and disposer for the planet.
But until recent studies, the conventional wisdom was that ice cover prevented the growth of phytoplankton for most of the year in the ocean around Antarctica because very little sunlight could penetrate to the water below. However, new evidence shows there are just enough cracks, thin spots and gaps to let sufficient daylight through the sea ice.
