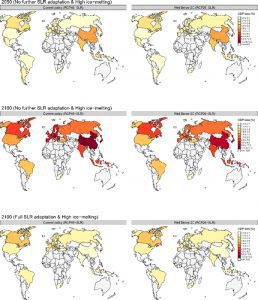
GDP impacts due to coastal flooding in G20 countries for 2050 and 2100 across climate policy scenarios in the cases of full and no further adaptation, and high ice-melting.
Rising sea levels, a direct impact of the Earth’s warming climate, is intensifying coastal flooding. The findings of a new study show that the projected negative economy-wide effects of coastal flooding are already significant until 2050, but are then predicted to increase substantially toward the end of the century if no further climate action on mitigation and adaptation is taken.
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015 by 175 parties, aims to limit global warming to well below 2°C compared to pre-industrial levels. However, the period 2010-2020 was the planet’s hottest decade on record, and the long-term trend is upward. Sea-level rise is one of the most severe impacts of climate change, with rising waters amplifying coastal floods, threatening coastal communities, infrastructure and agriculture.
New IIASA-led research for the first time assessed the economy-wide effects of sea-level rise globally and in particular in G20 countries when jointly taking into account different climate mitigation and adaptation assumptions, using three different macroeconomic models. In the study, authors compared two different climate policy scenarios—one achieving well below 2°C warming by the end of this century (basically in line with the Paris Agreement), and one overshooting this target—in combination with two different adaptation scenarios (no adaptation and full adaptation to sea-level rise) and estimated GDP impacts due to coastal flooding in all scenario combinations for 2050 and 2100. The study is also innovative in terms of looking at G20 countries explicitly—that is, countries that are big emitters and at the same time affected by climate change. The analysis thus corroborates the need for action on both mitigation and adaptation.
