 Fossil fuel combustion is the main contributor to black carbon collected at five sites around the Arctic, which has implications for global warming, according to a study by an international group of scientists.
Fossil fuel combustion is the main contributor to black carbon collected at five sites around the Arctic, which has implications for global warming, according to a study by an international group of scientists.
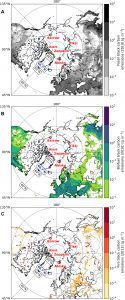
The five-year study to uncover sources of black carbon was done at five remote sites around the Arctic and is published in the journal Science Advances, a publication of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
The team from Baylor University used radiocarbon to determine fossil and biomass burning contributions to black carbon in Barrow, Alaska, while their collaborators used the same technique for sites in Russia, Canada, Sweden and Norway.
Findings showed that fossil fuel combustion (coal, gasoline or diesel) is responsible for most of the black carbon in the Arctic (annually around 60 percent), but that biomass burning (including wildfires and residential woodsmoke) becomes more important in the summer.
